The Bedrock of the Digital Enterprise: An Introduction to the Data Quality Management Industry
In today's data-driven world, organizations are increasingly realizing that their most valuable asset is not the raw data they collect, but the high-quality, trustworthy information they can derive from it. This realization has propelled the growth of the vital and sophisticated Data Quality Management industry. Data Quality Management (DQM) is the comprehensive business practice that combines technology, processes, and people to ensure that an organization's data is fit for its intended purpose. It is the formal process of discovering, controlling, and improving the quality of data across its entire lifecycle. The core principle behind DQM is the famous adage, "garbage in, garbage out." If an organization feeds its business intelligence tools, CRM systems, or advanced AI models with inaccurate, incomplete, or inconsistent data, the resulting reports, customer interactions, and predictions will be fundamentally flawed. DQM is the proactive discipline designed to prevent this, transforming data from a potential liability into a reliable, strategic asset that can be confidently used to drive business decisions, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. It is the essential, foundational layer upon which all successful data-driven initiatives are built.
The effectiveness of any DQM program is measured against a set of well-defined dimensions of data quality. These dimensions provide a framework for assessing and improving the "fitness" of the data. Accuracy is perhaps the most obvious, ensuring that data values correctly represent the real-world entity they describe—is the customer's name spelled correctly? Completeness refers to the absence of missing data; a customer record with a missing phone number or email address is incomplete and less useful. Consistency ensures that data is uniform and free from contradiction across different systems; a customer's address should be the same in the billing system as it is in the shipping system. Timeliness is critical for operational decisions, ensuring that data is up-to-date and available when it is needed. Validity confirms that data conforms to a defined set of business rules or formats, such as ensuring a date of birth is in the correct MM/DD/YYYY format. Lastly, Uniqueness focuses on eliminating duplication, ensuring that a single real-world entity (like a customer or a product) is not represented by multiple, conflicting records in the database. A comprehensive DQM strategy systematically addresses all of these dimensions to build a foundation of trusted data.
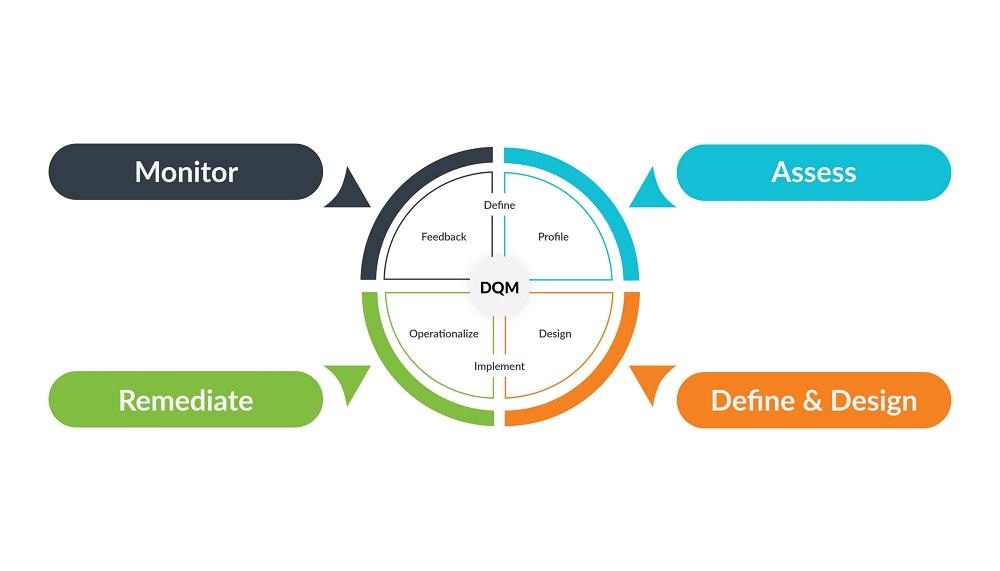
To achieve these quality dimensions, the DQM industry employs a cyclical, multi-stage process. The journey typically begins with Data Profiling. This is the initial discovery phase, where specialized software is used to scan and analyze datasets to understand their structure, content, and quality. Profiling reveals the true state of the data, identifying issues like null values, incorrect formats, and statistical outliers, which provides a baseline for improvement. The next stage is Data Cleansing and Standardization. This is the "fixing" phase, where the identified errors are corrected. This can involve parsing and reformatting data (e.g., standardizing address formats), correcting misspelled names, and validating information against reference data. The third stage is Data Matching and Linking. This powerful process uses sophisticated algorithms to identify and merge duplicate records, creating a single, consolidated "golden record" or "single source of truth" for each entity. The final stage is Data Monitoring. This is an ongoing process where data quality rules are continuously applied to the data, and dashboards are used to track quality metrics over time. This monitoring often includes a "data stewardship" workflow, where data quality issues are automatically routed to the responsible business users for remediation, embedding data quality as a continuous, enterprise-wide practice.
The impact of robust data quality management is felt across every department of an organization. For the marketing department, high-quality customer data is essential for effective personalization, targeted campaigns, and building a true 360-degree view of the customer. Inaccurate data leads to wasted marketing spend and a poor customer experience. For the finance and compliance teams, accurate data is non-negotiable for financial reporting, risk management, and meeting stringent regulatory requirements like GDPR, CCPA, and BCBS 239. Errors in financial data can lead to incorrect business decisions and severe regulatory penalties. In operations and supply chain management, high-quality data on products, inventory, and suppliers is critical for optimizing logistics, managing stock levels, and ensuring a smooth production process. Poor data in this area can lead to shipping errors, stockouts, and production delays. By providing a foundation of clean, consistent, and reliable information, the DQM industry empowers all of these business functions to operate more effectively, reduce risk, and make smarter, data-driven decisions that propel the entire organization forward.
Top Trending Reports:
Proximity Access Control Market
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness